A Ridge-based Approach for Extraction and Visualization of 3D Atmospheric Fronts
Anne Gossing, Andreas Beckert, Christoph Fischer, Nicolas Klenert, Vijay Natarajan, George Pacey, Thorwin Vogt, Marc Rautenhaus, and Daniel Baum.IEEE VIS, 2024, 176–180.
Best Paper Honorable Mention
Abstract
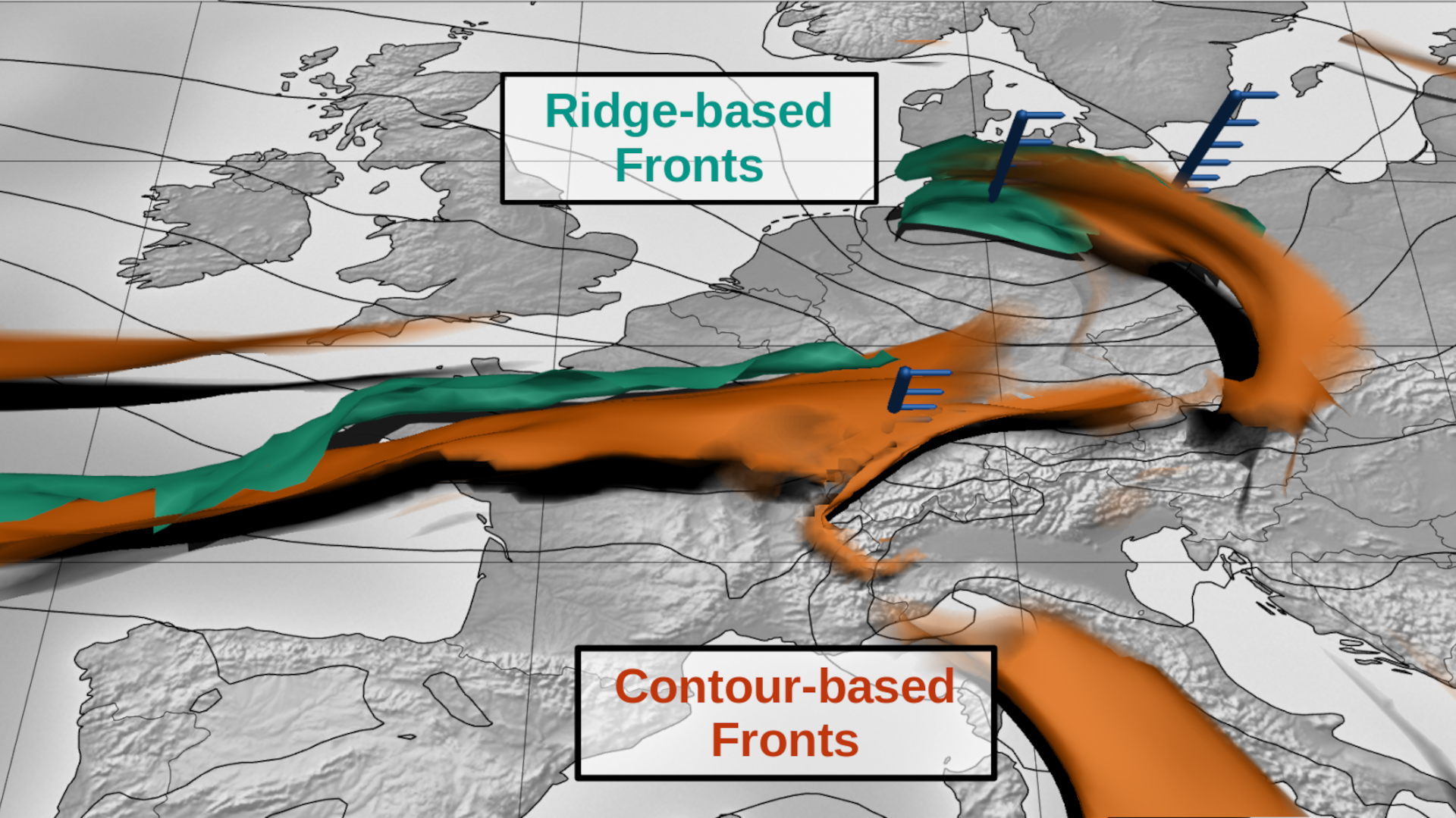
An atmospheric front is an imaginary surface that separates two distinct air masses and is commonly defined as the warm-air side of a frontal zone with high gradients of atmospheric temperature and humidity. These fronts are a widely used conceptual model in meteorology, which are often encountered in the literature as two-dimensional (2D) front lines on surface analysis charts. This paper presents a method for computing three-dimensional (3D) atmospheric fronts as surfaces that is capable of extracting continuous and well-confined features suitable for 3D visual analysis, spatio-temporal tracking, and statistical analyses. Recently developed contour-based methods for 3D front extraction rely on computing the third derivative of a moist potential temperature field. Additionally, they require the field to be smoothed to obtain continuous large-scale structures. This paper demonstrates the feasibility of an alternative method to front extraction using ridge surface computation. The proposed method requires only the sec- ond derivative of the input field and produces accurate structures even from unsmoothed data. An application of the ridge-based method to a data set corresponding to Cyclone Friederike demonstrates its benefits and utility towards visual analysis of the full 3D structure of fronts.[PDF]